What Is NCE-1 and How Does It Work?
New Chemical Entity (NCE-1) is an application submitted to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for a new drug. This process is also known as a paragraph IV filing. The NCE-1 drug represents a slight modification of an existing approved drug. The term “minus 1” implies that the New Chemical Entity (NCE) is only one small change away from an already FDA-approved and marketed drug.
The approval process for a para IV filing is comparatively quicker and cost-effective than that for entirely newly developed drugs. The time required for the para IV filing is reduced because the FDA may utilize efficacy and safety data available from the original drug.
Hence, this enables companies to bring new medicines to market quickly and affordably, thereby providing patients with new treatments sooner.
Why Does the NCE-1 Date Matter?
NCE-1 refers to the date, exactly one year before the end of the five-year exclusivity period.
For generic drug manufacturers, the NCE-1 date represents the earliest opportunity to file an Abbreviated New Drug Application (ANDA) with a Paragraph IV certification. This is a legal and regulatory move aimed at challenging the patents protecting the original drug.
For innovators, it is like a warning bell that signals the countdown to generic competition has begun.
Why Is the NCE-1 Date Important for Generic Drug Companies?
It can win a 180-day market exclusivity for the first generic filer.
Missing the NCE Minus 1 window implies missing out on a first-mover advantage in a competitive market.
Step-by-Step NCE-1 Filing Process
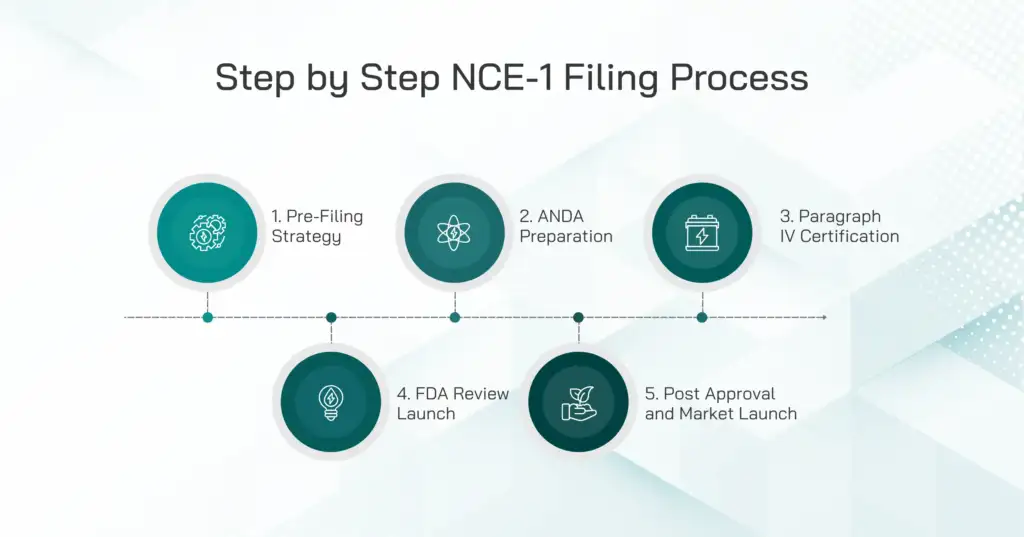
1. Pre-Filing Strategy and Preparation
Companies need to carry out groundwork before submitting the NCE-1 filing application, which includes:
- Reviewing relevant patents listed in the FDA’s Orange Book
- Analyzing the validity of those patents and identifying opportunities to challenge them
- Gathering data on the innovator’s regulatory history, clinical studies, and market position
This step requires close collaboration among regulatory teams, patent attorneys, clinical experts, and business strategists. This step can be automated by using our NCE-1 intelligence platform, NCE Grid.
2. Preparing the ANDA Application
This step is exactly where technical development comes into the picture:
- Developing a formulation that is bioequivalent to the innovator’s drug
- Conducting testing and gathering stability data
- Providing detailed chemistry, manufacturing, and control (CMC) documentation
These components serve as the foundation of the ANDA filings and must meet the FDA requirements.
3. Paragraph IV Certification
This step involves formally challenging the listed patents. This is done by asserting that they are invalid, unenforceable, or won’t be infringed by the generic version.
It’s a critical and complex legal process that often triggers litigation from the innovator company.
4. Submission to the FDA and Review
The ANDA application is submitted to the FDA, which reviews the data for:
- Consistency in manufacturing and quality
- Clinical equivalence to the original drug
- Proper labeling and documentation
This review usually involves back-and-forth communication between the generic pharmaceutical company and the FDA. This step can also include requests for clarification or additional studies required by the FDA.
5. Post-Approval and Market Launch
Once the ANDA is approved, the final steps include:
- Scaling up manufacturing
- Coordinating a successful market launch
- Addressing any ongoing patent litigation
The main goal of a para IV filing is to enter the market smoothly while ensuring compliance with all relevant regulatory and legal requirements.
Companies that understand and act on this timeline can establish themselves early in competitive markets, while others may struggle to catch up. With the right planning and expertise, this process can become a gateway to success.
Making NCE-1 Filing Easier with the NCE Grid
To simplify the tracking and planning process of the New Chemical Entity (NCE-1) drugs, Spring Bio Solution has launched the NCE Grid, an intelligence tool designed to support smarter decision-making.
Key Features of the NCE Grid
- Molecule name, innovator, dosage, strength, and indication
- NCE and NCE-1 dates
- Revenue insights, CAGR percentages
- Projected sales
It’s everything you need in one place to spot opportunities, plan NCE-1 filings, and take action before your competitors.
FAQs
What does NCE-1 mean?
NCE-1 is the date that falls exactly one year before the NCE’s 5-year exclusivity period expires. It’s the earliest date when generic drug companies can file applications to challenge the original drug’s patents and exclusivity.
Why is the NCE-1 date important for generic companies?
The NCE-1 date is crucial because it’s the first opportunity for generic manufacturers to file an ANDA (Abbreviated New Drug Application) with a patent challenge. Being the first to file can provide a 180-day exclusivity period for the generic company.
What is a Paragraph IV certification?
A Paragraph IV certification is a formal challenge that generic companies file, claiming the original drug’s patents are invalid, unenforceable, or won’t be infringed by their generic version. It’s part of the NCE-1 filing process.
How long does NCE exclusivity last?
NCE exclusivity typically lasts for 5 years from the date of FDA approval. During this time, the original pharmaceutical company had exclusive marketing rights, allowing it to recoup its research and development investments.
What happens after an NCE-1 filing is approved?
After the FDA approves the generic application, companies must prepare for market entry, which may involve patent litigation with the original drug company, scaling up manufacturing, and coordinating the commercial launch while meeting all relevant legal requirements.





